Agricultural extension programmes are quite diverse from an international perspective. Most are managed as public sector agencies, usually located in the ministry of agriculture, but some are located in other ministries such as education or rural development. Many are managed by nongovernmental organizations (NGOs). Many private firms and private organizations (for example, coffee-growers' associations) conduct extension programmes. Even within the most typical organizational structure, where extension is part of the government's ministry of agriculture, there is great variation in the degree of decentralization of management of extension services. In some countries, extension is decentralized, as in India, where it is a state subject. In most developing countries, however, governmental services are highly centralized, with varying forms of regional and subregional units designed to serve local areas.
Further, there is great variation in the skill level and agricultural competence of field staff. In some systems, field staff have little formal technical training in the agricultural sciences. In some cases, this is dictated by a village worker philosophy, in others by local language demands. But, in most cases, it simply is the result of the decisions to expand agricultural extension programmes rapidly during the 1950s and 1960s, when few highly trained agriculturalists were available (see Bindlish & Evenson, 1993 and Bindlish, Gbetibouo, & Evenson, 1993 for African studies; and Swanson & Claar, 1984 for a general history).
Finally, this diversity of skills, management systems, and objectives has changed over time in many countries. Perhaps the major changes in the management and design of agricultural extension systems over the past four decades is associated with the training and visit (T&V) system introduced in the 1970s by Benor, Harrison, and Baxter (1984) and implemented in many countries with World Bank lending support.
Given this diversity, broad generalizations about the economic contribution of agricultural extension to agricultural development are not feasible. Many situation-specific factors impinge on the effectiveness of extension programmes. The fact that substantial reform and redesign of many extension programmes has taken place indicates that some of them were perceived by their supporters to have been less than fully effective. However, we now have a substantial body of economic studies of extension services in a number of countries; 75 studies of economic impacts of extension systems have been published to date. My task in this chapter is to review the findings of 57 of these studies and to draw out some of the lessons they have to offer.
I begin this review with a brief summary of investment patterns for both agricultural research and extension. This is designed to provide historical perspective and to call attention to some of the economic and institutional diversity in which extension systems must function. In the second section, I review the conceptual foundation for measuring the economic impact. Statistical procedures are reviewed in the third section, and in the fourth I summarize the findings of the studies under review and attempt to relate these to some of the differences in economic and institutional settings. In the final part, I summarize policy lessons
Monday 31 March 2014
Study online
Modern agricultural extension
In the early years of this century, extension services were in their formative stage; they were relatively small in scale and limited in the scope of their work and contact with farmers, and their organization was often somewhat haphazard even though based on legislation. They were organized predominantly either by central or local governments, or by agricultural colleges, usually in close association with experiment stations, or by farmers' organizations (agricultural societies, cooperatives, farmers' unions, or chambers of agriculture), or combinations of these parent bodies. As the century has progressed, the organizations have matured. Changes have often occurred to their parent affiliations, government funding has become relatively more important, their objectives have become broader, especially in "the North," and the extension workers have become better trained and more professional. In addition, several other kinds of organizations have developed comparable work: agriculture-related commercial companies; agricultural commodity marketing boards, concerned to assure the supply and quality of their specific product; agricultural development projects, many of considerable territorial scale; and a variety of nongovernmental organizations (especially religious and charitable) involved in agricultural and rural development.
As agricultural extension organizations have grown and changed, they have invariably become more bureaucratic with distinct hierarchical structures. The work of dispersed extension workers had to be administered and controlled so that one or more levels of intermediary structure (for example, district, region) have been created between the field-level agents and their headquarters. Thus the management of extension activities has become a major preoccupation, and many organizations have been open to the criticism of being top heavy and top-down in their approach. However, with funding derived largely from national revenues (or international donors), senior managers have necessarily had to account for and justify their organization's activities. This has been equally pronounced in the North as in the South where, after colonial territories gained their independence, extension work has commonly been rein-vented and staffed by nationals under the aegis of their new administrations (usually ministries of agriculture).
During the past quarter century, the work of extension services has often become more diversified. In the less developed countries, the main focus remains on agricultural (mainly food) production, but there has been a growing recognition of the need to reach, influence, and benefit the multitudes of small, resource-poor farmers. Strong efforts have been made in this direction, notably through the training and visit system. Among the commercial farmers of the North, a major problem has become surplus production, with farmers facing economic and policy pressures to restrict it. Associated with intensive production methods, many issues and problems regarding environmental deterioration and livestock welfare have also arisen. Thus these have become important aspects of extension work, particularly socioeconomic guidance which focusses both on means by which farmers might maintain their income levels from their resources (for example, introduction of novel crops or livestock and involvement in various rural enterprises) and on the ways of assuring the longer term welfare of farmers and their families. Agricultural extension services are thus adding a strong social dimension to their activities.
Agricultural extension has now become recognised as an essential mechanism for delivering information and advice as an "input" into modem farming. Since commercial farmers can derive direct financial benefits from these inputs, there is a trend towards the privatization of the extension organizations, often as parastatal or quasi governmental agencies, with farmers being required to pay for services which they had previously received free of charge. This trend is strong in the North, and there are examples of it beginning in the South.
The pace of change in the organization, functions, strategies, and approaches of agricultural extension is clearly accelerating.
As agricultural extension organizations have grown and changed, they have invariably become more bureaucratic with distinct hierarchical structures. The work of dispersed extension workers had to be administered and controlled so that one or more levels of intermediary structure (for example, district, region) have been created between the field-level agents and their headquarters. Thus the management of extension activities has become a major preoccupation, and many organizations have been open to the criticism of being top heavy and top-down in their approach. However, with funding derived largely from national revenues (or international donors), senior managers have necessarily had to account for and justify their organization's activities. This has been equally pronounced in the North as in the South where, after colonial territories gained their independence, extension work has commonly been rein-vented and staffed by nationals under the aegis of their new administrations (usually ministries of agriculture).
During the past quarter century, the work of extension services has often become more diversified. In the less developed countries, the main focus remains on agricultural (mainly food) production, but there has been a growing recognition of the need to reach, influence, and benefit the multitudes of small, resource-poor farmers. Strong efforts have been made in this direction, notably through the training and visit system. Among the commercial farmers of the North, a major problem has become surplus production, with farmers facing economic and policy pressures to restrict it. Associated with intensive production methods, many issues and problems regarding environmental deterioration and livestock welfare have also arisen. Thus these have become important aspects of extension work, particularly socioeconomic guidance which focusses both on means by which farmers might maintain their income levels from their resources (for example, introduction of novel crops or livestock and involvement in various rural enterprises) and on the ways of assuring the longer term welfare of farmers and their families. Agricultural extension services are thus adding a strong social dimension to their activities.
Agricultural extension has now become recognised as an essential mechanism for delivering information and advice as an "input" into modem farming. Since commercial farmers can derive direct financial benefits from these inputs, there is a trend towards the privatization of the extension organizations, often as parastatal or quasi governmental agencies, with farmers being required to pay for services which they had previously received free of charge. This trend is strong in the North, and there are examples of it beginning in the South.
The pace of change in the organization, functions, strategies, and approaches of agricultural extension is clearly accelerating.
Result 2014
Download PDF Bise Rawalpindi 8th Class Result 2014, Rawalpindi Board 8th Class result 2014,
BISE Rawalpindi 8th Class result 2014:
The Board of intermediate and secondary education Rawalpindi conducts intermediate, upper primary, secondary and higher secondary examinations every year, All the schools are affiliated with this board function, under this board and organize the exams.The board of intermediate and secondary education Rawalpindi conducts the 8th class level in the month February every year. The Board declares the 8th calls results in 31st March 2014. Students can check the results on the Official website of the Board or on
Note: To Know about your result kindly Place your Roll Number below in Comment Box,
PEC Rawalpindi Board 8th Class Result 2014 Online Pdf Download
Download PDF Bise Rawalpindi 8th Class Result 2014, Rawalpindi Board 8th Class result 2014,
BISE Rawalpindi 8th Class result 2014:
The Board of intermediate and secondary education Rawalpindi conducts intermediate, upper primary, secondary and higher secondary examinations every year, All the schools are affiliated with this board function, under this board and organize the exams.The board of intermediate and secondary education Rawalpindi conducts the 8th class level in the month February every year. The Board declares the 8th calls results in 31st March 2014. Students can check the results on the Official website of the Board or on
Click For Result 8th 5th
Note: To Know about your result kindly Place your Roll Number below in Comment Box,
Tuesday 18 March 2014
Get €71,88 in your Skype account Free
HeLlo Everyone!
1) go to this link https://collaboration.skype.com/promotion
![[Image: 11uc0zk.png]](http://i41.tinypic.com/11uc0zk.png)
2) enter your Email id of Skype.. and press "SEND"
3) Sign in your email account.. (gmail, yahoo, hotmail etc)
4) open the new skype email and follow the setps.
5) login your Skype form Website.
And see you Got €71,88 in your Skype...And your account is Premium..
enjoy..
This is tested by me..
sreach:
Get €71,88 in your Skype account Free
Get €71,88 in your Skype account Free Hack
Get €71,88 in your Skype account hacking Tricks
Programmer

![[Image: dennis_ritchie.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjwm3LfbGti2EkSgcnm9H4orxoCeop871ZpsQOg3jce3wGpJY7XHOrgFUdwqdY5OhikXFv4qi15xPkzGTdduCVUjBsnMRrqkM4IVNaqYOPXpQdocIJVjlypE315wEZIcSDPv75i8yFBQXY/s320/dennis_ritchie.jpg)
Dennis Ritchie (1941-2011) was an American Computer Programmer. Sir. Ritchie developed "C" programming language and co-developer of Unix Operating system. Dennis Ritchie worked for Alcatel-Lucent and for Bell labs.
Dennis Ritchie changed digital era by creating "C" programming language. Lisp, Visual Basic, Pascal, COBOL, Turbo pascal 7.0, PL/1, ADA, these are the programming languages are written in C programming language. "C" is a best programming language for newbie programmers, Who are interested in learning codes.
Dennis Ritchie and his colleague Ken Thompson received the Turing award for implementing and developing UNIX operating system in the year 1983.
![[Image: Mark-Zuckerberg-507402-1-402.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiXdZqgZNSDsCpfodMnQtlv_tZyK_vI_hM9xXo5v7j0x3pQWeWdz12IhBEx3uD8m5vc0Kqij5p8tc9lUGG2B2GXbcGfhi1Prfu9BkP2mN1AlldzT9TUml2_KLIyBJdMouggZRhOg3sEf1I/s320/Mark-Zuckerberg-507402-1-402.jpg)
Mark Zuckerberg created Facebook.com when he was 20 years old, Mark and his Harward university friends helped to build Facebook. When Facebook started it was only available for Hardward students. Facebook website is mainly written in C++ and PHP programming language.
Mark is very passionate about programming and codes, In his early age he created a messenger called "Zucknet" that allowed to chat with all computers. In 2003 Mark created Facemash, the website is all about comparing two Harward university students side by side "Hot or Not" contest.
Some developers re-created Facemash (click it)
In last year Mark Zuckerberg earned more than $2 billion worth stock. And worth $15B according to report of usnews.
![[Image: 1296071-steve_wozniak05.jpg]](http://static.giantbomb.com/uploads/original/1/17172/1296071-steve_wozniak05.jpg)
The Brain behind Apple Inc. -Steve Wozniak is an Computer scientist and Programmer
Steve Woz is well known for developing Apple-1 and Apple-2 :
In early 1976 Woz and Jobs developed a Hardware ,Circuit Board design and Operating system for
Apple- 1 . Apple 1 priced around $666, And sold 50 system boards to Paul Terrell (Computer shop owner) . After Apple-1, Woz developed first Color graphics personal computer with Integer BASIC programming language and they named it as a Apple-2.
For sometime Steve Wozniak was teaching elementary school students about computer. In 2006 Steve Woz published his autobiography iWoz: From Computer Geek to Cult Icon. Now Steve Woz is working for Fusion-io as a Chief Scientist.
![[Image: billgates.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhVOQTJesih3ePRAy49d3JIbC20Qx4D3ypB9lIcmTSi8YxIhfjZJUM6iIWKDcoIUavjjHNf1PkaSMzUeWILaSJL911z6IoedWCHfLPd1fOOlxUsVCxY9v-upRgHJqqzFJtFLzppny9ve7vJ/s1600/billgates.jpg)
Bill Gates: Founder of world's largest software company Microsoft, And also Co-chairman of Gates Foundation. Also Bill gates is one of the world's richest man in the world.
Bill started working with computer when he was 13 years old. When he was 17 Bill Gates formed a company called Traf-o-data. And In the age of 20 Bill Gates founded Microsoft Inc. Bill Gates also created MS-DOS Operating system and Windows OS. Currently Microsoft is one of the valuable company in the world. In 2012 Microsoft earns $73.72 Billion.
![[Image: linus-torvalds.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEihRbxLCbjw6DqjfUVrJPSc34WjHuqeZYI77poQy9LG2ePo7fKA7yjwxNxiepWXsLDW8kvWL5wpNAXXFIerR4Nzwvm1cmVQkJOwOCCCFcR_RTHMLvafbYDL19aMc23Ef5yeMCfhHne3aln4/s320/linus-torvalds.jpg)
Linus Torvalds is a software engineer, hacker and project coordinator.
In 1991 Linus Torvalds released Linux 0.11 which is written in C programming language. Linux supports more than 20+ platforms. And Linux is a free and open source operating system, Open source means that you can get the source code of the operating system for free.
The Top 5 Programmers lists ends here according to me but there are thousands of best programmers like : Larry page, Brin sergy, Bjarne Stroustrup.
Top 5 Computer Programmers in the world

Top 5 Computer Programmers in the world.
1. Dennis Ritchie
![[Image: dennis_ritchie.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjwm3LfbGti2EkSgcnm9H4orxoCeop871ZpsQOg3jce3wGpJY7XHOrgFUdwqdY5OhikXFv4qi15xPkzGTdduCVUjBsnMRrqkM4IVNaqYOPXpQdocIJVjlypE315wEZIcSDPv75i8yFBQXY/s320/dennis_ritchie.jpg)
Dennis Ritchie (1941-2011) was an American Computer Programmer. Sir. Ritchie developed "C" programming language and co-developer of Unix Operating system. Dennis Ritchie worked for Alcatel-Lucent and for Bell labs.
Dennis Ritchie changed digital era by creating "C" programming language. Lisp, Visual Basic, Pascal, COBOL, Turbo pascal 7.0, PL/1, ADA, these are the programming languages are written in C programming language. "C" is a best programming language for newbie programmers, Who are interested in learning codes.
Dennis Ritchie and his colleague Ken Thompson received the Turing award for implementing and developing UNIX operating system in the year 1983.
2. Mark Zuckerberg
![[Image: Mark-Zuckerberg-507402-1-402.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiXdZqgZNSDsCpfodMnQtlv_tZyK_vI_hM9xXo5v7j0x3pQWeWdz12IhBEx3uD8m5vc0Kqij5p8tc9lUGG2B2GXbcGfhi1Prfu9BkP2mN1AlldzT9TUml2_KLIyBJdMouggZRhOg3sEf1I/s320/Mark-Zuckerberg-507402-1-402.jpg)
Mark Zuckerberg created Facebook.com when he was 20 years old, Mark and his Harward university friends helped to build Facebook. When Facebook started it was only available for Hardward students. Facebook website is mainly written in C++ and PHP programming language.
Mark is very passionate about programming and codes, In his early age he created a messenger called "Zucknet" that allowed to chat with all computers. In 2003 Mark created Facemash, the website is all about comparing two Harward university students side by side "Hot or Not" contest.
Some developers re-created Facemash (click it)
In last year Mark Zuckerberg earned more than $2 billion worth stock. And worth $15B according to report of usnews.
3. Steve Wozniak
![[Image: 1296071-steve_wozniak05.jpg]](http://static.giantbomb.com/uploads/original/1/17172/1296071-steve_wozniak05.jpg)
The Brain behind Apple Inc. -Steve Wozniak is an Computer scientist and Programmer
Steve Woz is well known for developing Apple-1 and Apple-2 :
In early 1976 Woz and Jobs developed a Hardware ,Circuit Board design and Operating system for
Apple- 1 . Apple 1 priced around $666, And sold 50 system boards to Paul Terrell (Computer shop owner) . After Apple-1, Woz developed first Color graphics personal computer with Integer BASIC programming language and they named it as a Apple-2.
For sometime Steve Wozniak was teaching elementary school students about computer. In 2006 Steve Woz published his autobiography iWoz: From Computer Geek to Cult Icon. Now Steve Woz is working for Fusion-io as a Chief Scientist.
4. Bill Gates
![[Image: billgates.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhVOQTJesih3ePRAy49d3JIbC20Qx4D3ypB9lIcmTSi8YxIhfjZJUM6iIWKDcoIUavjjHNf1PkaSMzUeWILaSJL911z6IoedWCHfLPd1fOOlxUsVCxY9v-upRgHJqqzFJtFLzppny9ve7vJ/s1600/billgates.jpg)
Bill Gates: Founder of world's largest software company Microsoft, And also Co-chairman of Gates Foundation. Also Bill gates is one of the world's richest man in the world.
Bill started working with computer when he was 13 years old. When he was 17 Bill Gates formed a company called Traf-o-data. And In the age of 20 Bill Gates founded Microsoft Inc. Bill Gates also created MS-DOS Operating system and Windows OS. Currently Microsoft is one of the valuable company in the world. In 2012 Microsoft earns $73.72 Billion.
5. Linus Torvalds
![[Image: linus-torvalds.jpg]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEihRbxLCbjw6DqjfUVrJPSc34WjHuqeZYI77poQy9LG2ePo7fKA7yjwxNxiepWXsLDW8kvWL5wpNAXXFIerR4Nzwvm1cmVQkJOwOCCCFcR_RTHMLvafbYDL19aMc23Ef5yeMCfhHne3aln4/s320/linus-torvalds.jpg)
Linus Torvalds is a software engineer, hacker and project coordinator.
In 1991 Linus Torvalds released Linux 0.11 which is written in C programming language. Linux supports more than 20+ platforms. And Linux is a free and open source operating system, Open source means that you can get the source code of the operating system for free.
The Top 5 Programmers lists ends here according to me but there are thousands of best programmers like : Larry page, Brin sergy, Bjarne Stroustrup.
account hacking, Gmail Hacking, Hacking
in this part
First things first, then. Before you get into the deeper workings
of Gmail, you need to get yourself up to scratch with
the more public side of the application. Being able to hack
Gmail is one thing, but it’s very helpful to have a full understanding
of how the system is meant to work before taking it apart and
doing silly things with it.
In this part, therefore, you look at how to integrate Gmail
with your desktop (Chapter 1). Then in Chapter 2 you look at
merging your existing mail into the application, and finally in
Chapter 3 you look at some of the cunning ways people use
Gmail to its utmost.
in this chapter
that the Gmail service, although ostensibly a website, can
be dragged over to touch the desktop in ways that make
new and exciting applications possible.
The first five chapters deal with this on a very basic level, allowing
you to use Gmail to its limits before delving into the nitty
gritty of code and some rather extreme uses of the system.
This chapter deals with the situations that arise when you continue
to use Gmail within the browser but want to use it as your
day-to-day e-mail system. There are two areas to cover: new mail
notification and mailto: link redirection.
their entire e-mail regime over to the service. But unlike other
e-mail clients, Gmail requires you to have your web browser open
to see if you have any new mail. Even with tabbed browsing, this
is annoying. The alternative is to use a new-mail notifier application.
This section details some of the best notifiers, grouped by
platform. This is not a definitive list even at the time of this writing.
By the time you read this, there will be even more options.
But this is a good start.
book, but certainly one with a lot of users,Windows is gifted with
a wide range of Gmail integration products.
The first and most obvious application comes from Google itself. Their Gmail
Notifier sits in the system tray, and displays an unread mail count, and the subject
line, sender, and a synopsis of newly arriving mail, all shown in Figure 1-1. At
the time of writing, it, like Gmail itself, is in beta. Get the Gmail Notifier from
http://toolbar.google.com/gmail-helper/.
FIGURE 1-1: Google’s own Gmail Notifier in action
FIGURE 1-3: Gmail Status in action, with Growl notification
Nathan Spindel’s gCount (www.ocf.berkeley.edu/~natan/gcount/), shown
in Figure 1-4, is very similar indeed to GmailStatus in terms of functionality, with
perhaps two interesting additions. First, you can have a new mail count in the
dock, and second, it takes your Gmail username and password from the keychain.
This is a nice touch.
compile things, have a whole series of potential Gmail applications to choose
from. Linux users will also find the scripting done in the later stages of this book
to be very simple to implement.
FIGURE 1-4: gCount, showing the preference menu
FIGURE 1-7: GmailerXP in action
Part I
part I
in this part
C
hapter 1
Desktop Integration
Chapter 2
Integrating Your
Existing Mail
Chapter 3
Starting to Use Gmail
Gmail Power TipsFirst things first, then. Before you get into the deeper workings
of Gmail, you need to get yourself up to scratch with
the more public side of the application. Being able to hack
Gmail is one thing, but it’s very helpful to have a full understanding
of how the system is meant to work before taking it apart and
doing silly things with it.
In this part, therefore, you look at how to integrate Gmail
with your desktop (Chapter 1). Then in Chapter 2 you look at
merging your existing mail into the application, and finally in
Chapter 3 you look at some of the cunning ways people use
Gmail to its utmost.
chapter 1
in this chapter
New mail
notification
Available
applications
Redirecting mailto:
Desktop Integration
The first part of this book really highlights its entire theme:that the Gmail service, although ostensibly a website, can
be dragged over to touch the desktop in ways that make
new and exciting applications possible.
The first five chapters deal with this on a very basic level, allowing
you to use Gmail to its limits before delving into the nitty
gritty of code and some rather extreme uses of the system.
This chapter deals with the situations that arise when you continue
to use Gmail within the browser but want to use it as your
day-to-day e-mail system. There are two areas to cover: new mail
notification and mailto: link redirection.
New Mail Notification
Gmail’s great features have inspired many early adopters to movetheir entire e-mail regime over to the service. But unlike other
e-mail clients, Gmail requires you to have your web browser open
to see if you have any new mail. Even with tabbed browsing, this
is annoying. The alternative is to use a new-mail notifier application.
This section details some of the best notifiers, grouped by
platform. This is not a definitive list even at the time of this writing.
By the time you read this, there will be even more options.
But this is a good start.
Windows
Perhaps not the operating system of choice for the readers of thisbook, but certainly one with a lot of users,Windows is gifted with
a wide range of Gmail integration products.
Part I — Starting to Use Gmail
Google Gmail NotifierThe first and most obvious application comes from Google itself. Their Gmail
Notifier sits in the system tray, and displays an unread mail count, and the subject
line, sender, and a synopsis of newly arriving mail, all shown in Figure 1-1. At
the time of writing, it, like Gmail itself, is in beta. Get the Gmail Notifier from
http://toolbar.google.com/gmail-helper/.
FIGURE 1-1: Google’s own Gmail Notifier in action
Mozilla Extension Gmail Notifier
Technically, this will work on any platform that can run Mozilla-based browsers, but
I’ll put Doron Rosenberg’s Gmail Notifier browser extension here (see Figure 1-2).
Although it doesn’t provide the same level of interface as a taskbar-based application,
for people who spend a lot of time in their web browser, the Mozilla extension
is very convenient.
You can find the extension at http://nexgenmedia.net/extensions/.
Chapter 1 — Desktop Integration
doing pretty much the same thing: placing the mail notification in the menu bar
at the top of the screen.
guenther/GmailStatus/) is a good example. It displays new mail counts for the
Inbox, and each individual label you might have set up, adds a hotkey to launch
Gmail in your browser, supports Growl notifications (see http://growl.info/
for more on that), and gives a hotkey to write a new message in Gmail (see Figure
1-3).
FIGURE
Mac OS X
OS X users have a choice of two applications, both very similar to each other, anddoing pretty much the same thing: placing the mail notification in the menu bar
at the top of the screen.
GmailStatus
Carsten Guenther’s GmailStatus (http://homepage.mac.com/carsten.guenther/GmailStatus/) is a good example. It displays new mail counts for the
Inbox, and each individual label you might have set up, adds a hotkey to launch
Gmail in your browser, supports Growl notifications (see http://growl.info/
for more on that), and gives a hotkey to write a new message in Gmail (see Figure
1-3).
FIGURE
FIGURE 1-3: Gmail Status in action, with Growl notification
gCount
Nathan Spindel’s gCount (www.ocf.berkeley.edu/~natan/gcount/), shownin Figure 1-4, is very similar indeed to GmailStatus in terms of functionality, with
perhaps two interesting additions. First, you can have a new mail count in the
dock, and second, it takes your Gmail username and password from the keychain.
This is a nice touch.
Linux, etc.
People using Linux, or any other Unix-style operating system with the option tocompile things, have a whole series of potential Gmail applications to choose
from. Linux users will also find the scripting done in the later stages of this book
to be very simple to implement.
Part I — Starting to Use Gmail
FIGURE 1-4: gCount, showing the preference menu
Mail Notification
Jean-Yves Lefort’s Mail Notification system for Linux desktops supports Gmail
as well as most of the other common e-mail systems. You can get it from www.
nongnu.org/mailnotify/ where it is released under the GPL. According to
Lefort, it works with system trays implementing the freedesktop.org System
Tray Specification, such as the Gnome Panel Notification Area, the Xfce
Notification Area, and the KDE System Tray.
Wmgmail
Remarkably useful for the clarity of its Python-based code, Pasi Savolainen’s
Wmgmail is intended for use with WindowMaker or fluxbox window managers
on the operating system of your choice. (If that sentence means nothing to you,
this is not for you, in other words.)
It’s a standard new mail notification app, with new mail preview added in, but it
also has one very nice feature that is perfect for the hacker: You can set it to run
another program whenever new mail arrives.
You can find Wmgmail at http://osx.freshmeat.net/projects/wmgmail/
Redirecting mailto:
Now that you have your desktop telling you when you have new mail within your
Gmail account, the only remaining integration is to ensure that clicking on a
mailto: link on a web page opens Gmail instead of your operating system’s
default e-mail client.
Chapter 1 — Desktop Integration
Windows
Again, as with new mail notification,Windows users have the pick of the crop.
The Google-authored Gmail Notifier, as mentioned previously, gives you the
option to redirect mailto: links when you install it.
If you really want to, you can manually edit the Windows Registry to enact the
same effect. The website www.rabidsquirrel.net/G-Mailto/ gives a rundown
of just how to do this.
Multiplatform/Mozilla
Other than the Mozilla extension, at the time of this writing there is no mailto:
link diversion for the Linux desktop. But happily, by far the best way of repurposing
mailto: links is to do it in the browser, and specifically in a Mozilla-based
browser, which runs on all of the platforms used in this book:Windows, OS X,
and Linux. The platforms can use Jed Brown’s WebMailCompose extension (see
Figure 1-5), installable from http://jedbrown.net/mozilla/extensions/
#WebMailCompose.
Part I — Starting to Use Gmail
This extension also allows mailto: links to point to many other web-based
e-mail systems, should you tire of all of this coolness.
OS X
GmailStatus, mentioned earlier, also has the effect of changing mailto: links
to launch Gmail instead of Mail.app. But if you don’t want to use GmailStatus,
a good example for OS X users is Gmailto, found at http://gu.st/code/
Gmailto/. Gmailto is simple to use: Just download and run it, and then go to
Mail.app’s preference panel to change the default reader application to Gmailto
(displayed in Figure 1-6) instead of Mail.app.Why the preference panel is inside
the application you no longer wish to use is beyond the reckoning of mortal men.
GmailerXP
Well worth its own section, if only because it’s really weird, the Windows software
GmailerXP—http://gmailerxp.sourceforge.net—does all of the above
but adds in a desktop version of all of the other Gmail features as well: labels,
stars, setting filters and contacts, and so on (see Figure 1-7). I’m not sure when
you would use it, but it is a brilliant example of a Gmail hack.
The second half of this book looks at how applications such as GmailerXP work
and how to make your own.
Chapter 1 — Desktop Integration
FIGURE 1-7: GmailerXP in action
And Now . . .
By now you should be happily using Gmail, with new mail showing up on your
desktop and mailto: links on the web causing Gmail to open, not the default
mail reader you got with the operating system. In the next chapter, you look at
using the POP interface to pull your Gmail mail down into that very reader.
account hacking, Gmail Hacking, Hacking
Desktop Integration
Hacking Gmail
Hacking Gmail
Trademarks: Wiley and the Wiley logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of John Wiley & Sons, Inc. and/or its affiliates, in the UnitedStates and other countries, and may not be used without written permission. ExtremeTech and the ExtremeTech logo are trademarks of Ziff
Davis Publishing Holdings, Inc. Used under license. All rights reserved. Gmail is a trademark of Google, Inc. All other trademarks are the
property of their respective owners.Wiley Publishing, Inc., is not associated with any product or vendor mentioned in this book.
About the Author
Armed only with a PowerBook and some fine pipe tobacco, Faizan zafar is a
journalist, writer, explorer, and an errant developer and explainer of semantic web
technology. He’s also liable to spread his dirty, dirty words over at The Guardian.
As an Englishman of the clichéd sort, Ben’s angle brackets always balance, and his
tweed is always pressed. He’s not worn trousers for six months now. Ask him
about it sometime.
Contents at a Glance
Acknowledgments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Part I: Starting to Use Gmail . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 1,2,3
Desktop Integration
Integrating Your Existing Mail
Gmail Power Tips
Part II: Getting Inside Gmail
Chapter 4: Skinning Gmail
Chapter 5: How Gmail Works
Chapter 6: Gmail and Greasemonkey
Chapter 7: Gmail Libraries
Chapter 8: Checking for Mail
Chapter 9: Reading Mail
Chapter 10: Sending Mail
Part III: Conquering Gmail
Chapter 11: Dealing with Labels
Chapter 12: Addressing Addresses
Chapter 13: Building an API from the HTML-Only Version of Gmail
Chapter 14: Exporting Your Mail
Chapter 15: Using Gmail to
Chapter 16: Using GmailFS
Contents
click to Every Chapter and wait 5 sec click to Skip Ad after click skip Ad you Read the Chapter.
Acknowledgments
Books of this nature are tremendously difficult to write.Without support from
Google (we didn’t ask, admittedly) and with Gmail being in perpetual Beta
throughout the writing process, we often found ourselves with chapters being
made obsolete overnight. Deadlines passed, were rescheduled, passed again.
Editors wept salt tears. Publishers, that sainted breed, were patient and handsome
and generally lovely. Chris Webb and Brian Herrmann, both of the Wiley clan,
stood by the project so faithfully that their names will be forever legend. Men of
the Far North will sing songs to their honor. Justin Blanton, the technical editor,
managed to combine a Law Degree with the task: there’s not enough beer in the
world to pay him back. Thanks to all of them, and everyone else at Wiley.
Introduction
Welcome to Hacking Gmail. Thanks for buying this book. If you haven’t bought it,
you should. It’s very good, and once you buy it you can stop loitering around the
bookstore stacks. Go on: Buy it, sit down, have a coffee. See? Comfier isn’t it? Ah.
Hacking Gmail. It’s a manly hobby, and this book will tell you how. Sorry? What’s
Gmail, you ask? Well, let me tell you . . .
What’s Gmail?
March 31, 2004. A watershed in human history. Google’s web-based e-mail service,
still now at the time of this writing in Beta, and available only to people
invited by other existing users, was launched. Offering a gigabyte of storage, an
incredibly advanced JavaScript interface, and a series of user interface innovations,
Gmail was an instant hit among those who could get access to the system.Today,
more than a year later, Gmail is proving to be one of the flagship applications on
the web—a truly rich application within the browser, combined with the serverbased
power of the world’s leading search engine.
Hacking Gmail?
Of course, all that power just begs to be abused. Power corrupts, as they say,
and hackers are nothing but a corrupt bunch: Almost as soon as Gmail was
launched, hackers were looking at ways to use those capabilities for other purposes.
They investigated the incredibly rich interface, and saw how much of the processing
is done on the user’s own machine; they burrowed into the communication
between the browser and the server; and they developed a series of interfaces for
scripting languages to allow you to control Gmail from your own programs.
This book shows what they did, how to do it yourself, and what to do after you’ve
mastered the techniques. Meanwhile, you’ll also learn all about Ajax, the terribly
fashionable JavaScript technique that Gmail brought into the mainstream.Two
topics for the price of one!
What’s in This Post?
There are three parts to this Post, each lovingly crafted to bring you, young Jedi,
to the peak of Gmailing excellence. They are:
xx Introduction
Part I: Starting to Use Gmail
Where you learn to use Gmail like a professional. A professional Gmail user, no
less. A really skilled professional Gmail user.With a degree in Gmail. A Gmail
ninja. A Gmail ninja with a black belt in Gmail from the secret Gmail training
school on Mount Gmail. You might actually be part Gmail. Perhaps you’ve named
your first born child after Gmail. You live in the Google Headquarters. You are
Larry Page. You get the idea.
Part II: Getting Inside Gmail
Where you find out how Gmail works, and how you can use modern scripting
languages to control it.
Part III: Conquering Gmail
Where you put these new skills to the test, wrangling Gmail into fiendishly clever
uses, totally unlike those Google intended.
Whom Is This Book For?
You. Of course it is. If you picked up a book called Hacking Gmail, you’re very
likely to want it. If you’re a programmer looking to use Gmail in wacky ways, this
book is for you. If you’re a power user looking to hack together scripts to do dangerously
efficient things with your mail, this book is for you. If you’re the parent,
best friend, or lover of someone who answers to that description, this book is for
them, and you should buy two copies. Really. It’s great. And the shiny cover looks
cool, no? I tell you, metallic covers are all the thing.
Hacking Carefully
It must be said here in plain English, and elsewhere by a battalion of scary lawyer
folk, that I take no responsibility whatsoever for anything anyone does after reading
this book. If you lose data; get folded, spindled, or mutilated; or have your Gmail
account suspended, it is not my fault. The fine folks at Google, it has to be said,
have played no part in the writing of this book, and most likely do not approve of
the contents within. They may have me killed. Either way, I take no responsibility
for anything. You’re on your own, kiddo. As am I.
Companion Website
For links and updates, please visit this book’s companion website at www.wiley
Monday 17 March 2014
Sunday 16 March 2014
Blogger
How to Show Author Image in Google Search Results
Google is one of the biggest search engine in whole world and introduce some amazing features with the passage of time. Some months ago Google introduce Google Authorship for webmaster and bloggers and help them to provide better features. You notice when you search any keyword in Google then you got some sites in search results with author image and these sites owners are use Google authorship to display their profile picture in search results. Here we will going to show you a method to display your own image in search results by verifying Google authorship. You can also check our site in Google and you can see my image will appear with each post because we already verify our site in Google authorship. If you also want to verify Google authorship then simply follow below methods.
Also Read: How to Make Blogger Template SEO Friendly?
Methods to Verify Google Authorship.
In order to getting Google authorship, first of all you need Google plus account. You need to set up your profile picture on Google plus because your blogger account is directly connected to Google+ profile. Here we will discuss some methods that will help you to verify Google authorship, just follow bellow steps and learn a method to display image in search results.
Method#1: Add Google+ Widget in your Blog:
This is one of the best and simple method to verifying Google authorship. You can simply add your Google+ profile badge in your blog and it will help Google to understand that this is your site. We suggest you to add your profile badge in sidebar. If you don’t know a method to add Google+ badge then simply follow below steps and learn a method to add Google+ badge in sidebar.
1. First of all Go to Blogger Dashboard>> Layout>> Add Gadget.
2. Scroll down and you can see Google+ Badge, simply click on it.
3. You can see some setting, just make your desired changes and click on save.
4. Know you’re done.
Method#2: Add your Site Link in Google+ Profile:
This is also one another method to verify Google authorship and sometimes it will also help you to gain quality backlinks from Google+. You just need to put your site link in your Google profile links and Google automatically detect it. If you don’t know a method to add your site in Google+ profile then simply follow below steps.
1. Login to your Google+ account.
2. Go to About Page.
3. Scroll down and your can see link section, just click on Edit.
4. After it one popup will appear, simply put here your site link and click on save.
5. Know you are successfully add your site in Google+ profile.
Method#3: Use rel='author' Attribute In About Us Page:
The rel='author' attribute are also help us to verify our Google authorship. You just need to put rel='author' attribute where you already add your Google+ profile link. If you don’t know a method to add this attribute then simply follow below steps.
1. Go to Blogger Dashboard>> Your Page>> Edit.
2. Know move to HTML tab and add below coding where you want to add Google link.
<a href="https://plus.google.com/GOOGLE+ ID/" rel='author' target=' _blank' >Your Name Goes Here</a>
3. Replace https: //plus.google.com/GOOGLE+ ID/ with your profile url.
4. Replace Your Name Goes Here with your name.
5. Know simply click on Publish or update.
Method#4: Use Domain Email to Verify Google Authorship:
This is our last method to verify Google authorship but if you still using blogger and don’t have hosting account then just use above 3 methods to verify your authorship but if you have web hosting account and your own domain email then you can also verify your authorship by using it. Just follow below steps and learn a method to verify authorship by using your domain email.
1. Login to your Google+ account.
2. Go to Google authorship.
3. Know a one page will appear, where you need to enter your domain email. Your domain will look like “name@yourdomain.com”. After entering a domain in specific field then simply click on Sing up for Authorship. You can also read some instructions that are given on their page.
4. After it you will receive an email with confirmation link.
5. Simply open email and click on confirmation link and one massage will appear in next window that you’re successfully verifying your Google authorship.
Check Your Google Authorship Status.
When you done above all steps successfully then just wait for one week and after it your image will be displaying in search results with each post of your site but you can simply check it here for confirmation that you're done all steps correctly or not.
1. Go to Structured Data Testing Tool
2. Enter your site URL and click on “Preview”.
3. Know you can see your image will be appear in results. If its show an error or don’t displaying results then find out error and fix it by reading again above methods deeply.
Need Help?
We hope these methods will help you to verify your Google authorship and if you’re enjoying this tutorial or you have any question then feel free to ask in comment section and share this post with your friends.
Best Wishes and Happy Blogging!
Web Designing
How to Create Social Networking Site Like Facebook
Facebook is one of the biggest social networking site in whole world and got millions of visitors daily and if you thinking about to start one website that look like same as facebook so you are on right place because today I am going to show you a method that how you cancreate social networking site and how you can manage it.
Facebook Is founded by Mark Zuckerberg in February 4, 2004, when he was attended in collage and know today facebook have 2 alexa rank and every person in the world who use internet must open facebook in their browser and use it for different resources. You can also make one website that have some great features such as facebook and manage all users’ accounts, who registered on your site.
Also Read: How to Make Money Online With Twitter
Create Website Like Facebook, Twitter and MySpace:
First of all you must need to purchase web hosting from any reliable company that provides some great features for your social networking site. You can also use free web hosting provider websites but if you going to set up one biggest website then must purchase web hosting. You can purchase web hosting from any reliable company but I recommended bluehost and hostgator because they have some amazing features for your social networking site.
When you purchase web hosting and domain name for your site then they will provide you CPanel, where you got a lot of scripts and software’s and by using these software’s you can set up every type of website that you want just like Video sharing, Social networking, E-commerce and forum sites in just few minuets and we will soon share some amazing ideas about how you can create these type of sites in our upcoming posts but today we will going to show you a method of creating social networking site.
Method to Create Social Networking Website:
Here is fully method that helps you to set up your own social networking site, you can set up your social site in just few click. Actually we make our site by using some auto installer software’s that set up your any type of website on wordpress, Joomla, drupal or anywhere else, where you want but we use these auto installer software’s for making social network site.
1. First of all log-in to your CPanel.
2. Know find “Softcalous or Fantastico” software under in “Software/ Services”. These both are same and install your any type of website in just few clicks.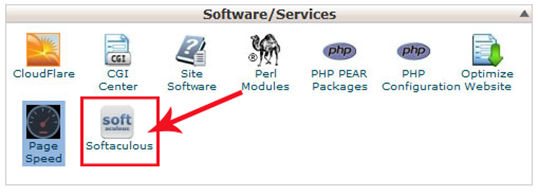

3. After it you can see a list of some popular scripts but you need to find “Social Networking” that may appear in your left sidebar, just click on it.
4. Know you can see a list of some popular community software’s just like Dolphin, Elgg, Jcow, Oxwall, Beatz, PeoplePods, Etano and many more, just select one of them. You can also see a demo of these all before selecting. Here we will going to Install Dolphin. You can select any software that you like and simply click on Install, same as below screenshot.
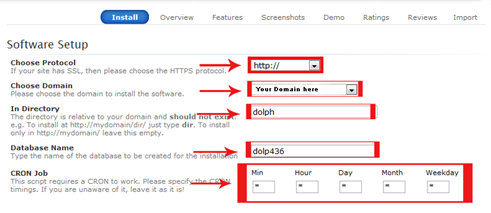
5. After it you can see “Software Setup” where you need to write some information about your site. Here you need to choose your desired protocol, your Domain and Database name and one thing keep in mind don’t change “Cron Job” because it will show error. You need to done whole process same as below screenshot.
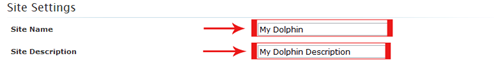
6. Know in “Site Setting” you need to write your site name and description, same as below screenshot.
7. After it you can see “Admin Account” where you need to set your Admin username, password and E-mail, just change them and click on install, same as below screenshot.
8. After it your installation will be start and it will take 3 or 4 minuets and then its display “Congratulations” massage and know your site will be successfully created.
Know you are owner of one Social networking site, where worldwide peoples are easily sign-up and manage their accounts and make discussion with different peoples same as facebook.
Need Help?
We hope you can easily understand whole method because its so simple and easy, however if you face any problem then feel free to ask in comment section and don’t forget to subscribe us because you can got daily some amazing and spicy tutorials directly to your inbox.
Best wishes!
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)